LiMnPO4
2020-02-06 13:10:07
The lithium manganese phosphate series mainly include LiMn (PO3) 3 (where manganese is divalent), LiMnP2Oy (where manganese is trivalent), and LizMn (PO3) 4. The synthesis of hydrated lithium manganese phosphate is limited, and only two compounds are synthesized, namely LiMnP6O18 · 10H2O (where manganese is divalent) and LiMn (OH) PO4 (manganese is trivalent).
Of interest is LiMnPO4 with an olivine structure. The crystal structure is composed of a deformed hexahedron densely packed oxygen framework. Li and Mn are located at half of the octahedral points, that is, the 4a and 4c positions. The 1/8 tetrahedron point is P. Along the b axis is the direction of preferential diffusion of lithium ions. The unit cell parameters are a = 0.1045nm, b = 0.0611nm, and c = 0.0475nm. There are slight differences in different literatures. In the PO4 tetrahedron, the three P--O bonds have the same length, which is 0.1546 nm, and the other is 0.1526 nm. First-principles calculations show that LiFePO4 is a semiconductor with a band gap of approximately 0.3 eV, LiMnPO4 is an insulator, and the band gap is 2 eV, which may be the main resistance to the redox reaction at its 4.1 V potential. Compared with LiMnPO4 and MnPO4, Lio.5MnPO4 has the smallest band gap. The JT deformation of Mn3 in LixMnPO4 is also very serious. The MO bond lengths in the MO6 octahedron are 0.213nm, 0.213nm, 0.222nm, 0.216nm, 0.209nm, and 0.244nm.
The magnetic properties of LiMnPO4 are the result of a special layered arrangement of Mn ions, which may have a dominant intra-layer MnMn exchange interaction. Below Neel temperature, three-dimensional magnetic ordering results from interlayer exchange. Mn ions form a two-dimensional tetragonal lattice on the bc plane, and the minimum distance between Mn and Mn is 0.392 nm, as shown in FIG. 1. Along the a-axis, the inter-layer Mn-Mn distance is much larger, which is 0.562 nm. A large Mn-Mn distance results in a weak MnMn exchange interaction. LiMnPO4 with an olivine structure is a quasi-two-dimensional Mn ion accumulation and contains important interlayer exchange. Not all Mn ions on the bc plane are at the same level, because the Mn layer is wrinkled, causing the MnO octahedron to tilt in different directions. This structure supports the anti-ferromagnetic structure of quasi-two-dimensional divalent manganese ions (S = 5/2), and has a considerable interlayer exchange interaction. In contrast, the magnetic properties of LiFePO4 are different, and the collinear antiferromagnetic order in LiFePO4 is stronger. Various defects in LiMnPO4 can lead to the appearance of weak ferromagnetic properties. The Neel temperature of LiMnPO4 is about 35K.
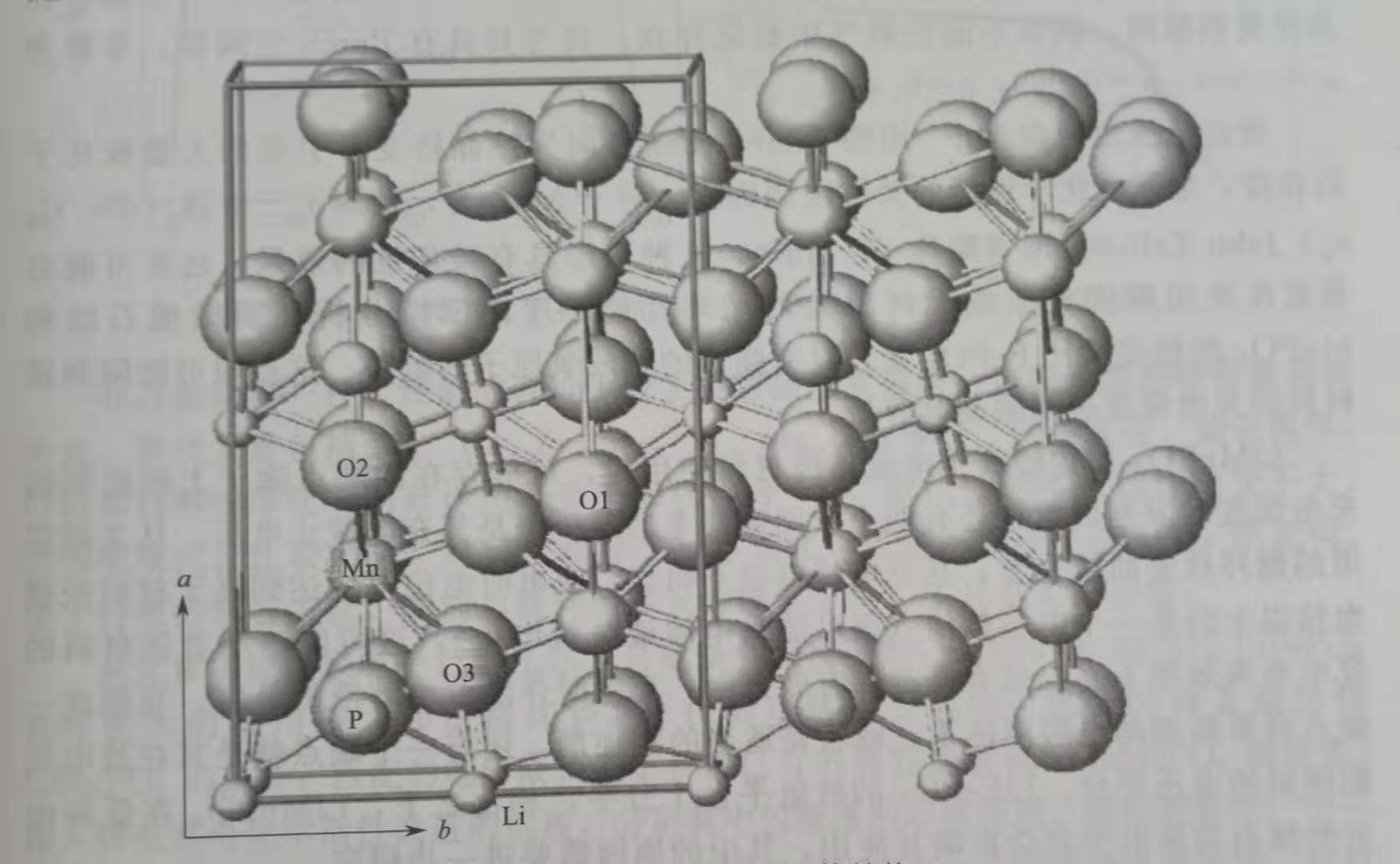
Fig.1 LiMnPO4 crystal structure
-
skype
Zale Zhou
